Neus代码的理解
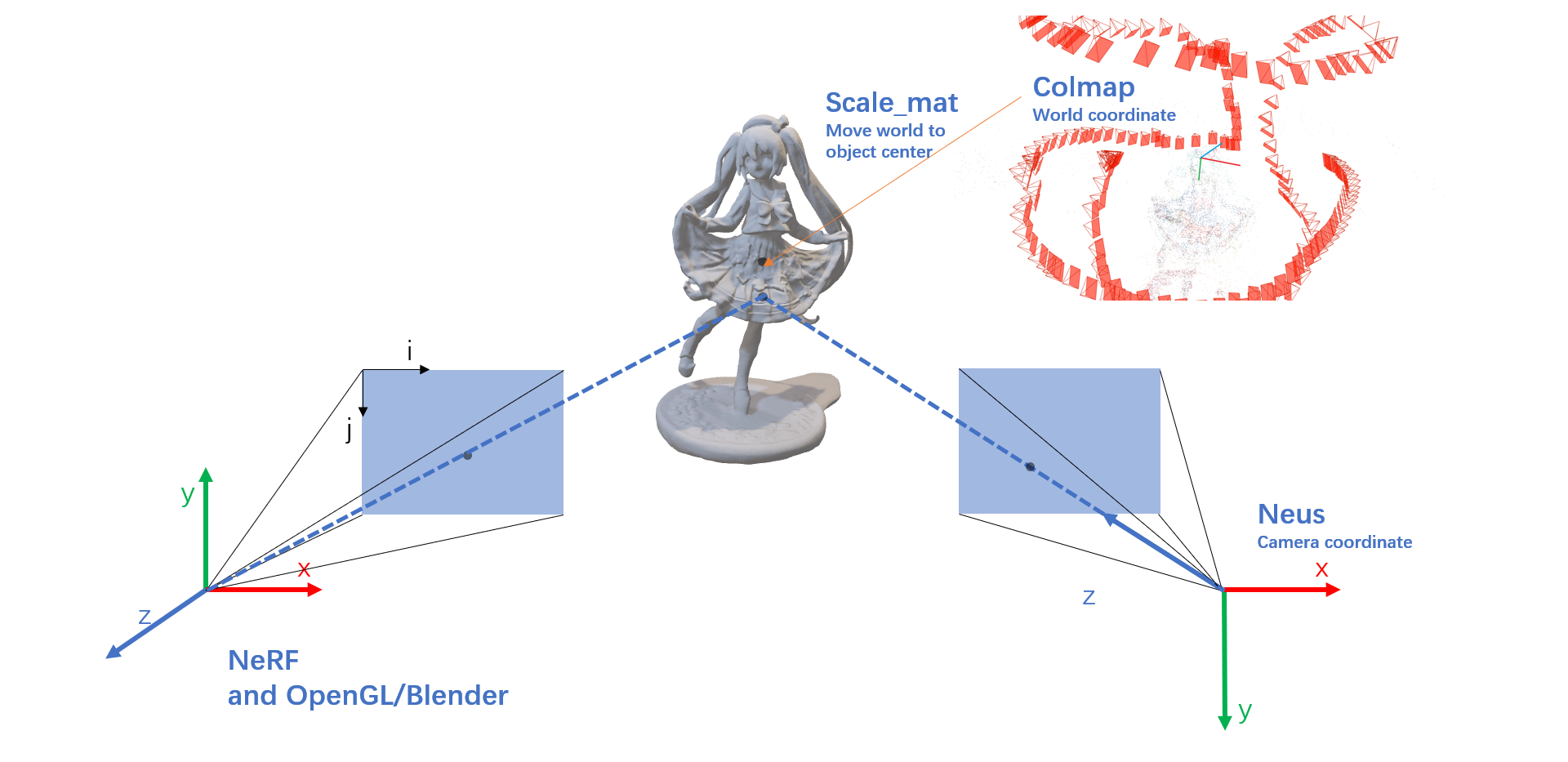
NeRF与Neus相机坐标系的对比:
| Method | Pixel to Camera coordinate |
|---|---|
| NeRF | $\vec d = \begin{pmatrix} \frac{i-\frac{W}{2}}{f} \\ -\frac{j-\frac{H}{2}}{f} \\ -1 \\ \end{pmatrix}$ , $intrinsics = K = \begin{bmatrix} f & 0 & \frac{W}{2} \\ 0 & f & \frac{H}{2} \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \\ \end{bmatrix}$ |
| Neus | $\vec d = intrinsics^{-1} \times pixel = \begin{bmatrix} \frac{1}{f} & 0 & -\frac{W}{2 \cdot f} \\ 0 & \frac{1}{f} & -\frac{H}{2 \cdot f} \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} i \\ j \\ 1 \\ \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} \frac{i-\frac{W}{2}}{f} \\ \frac{j-\frac{H}{2}}{f} \\ 1 \\ \end{pmatrix}$ |
Code
Runner().train流程图
数据集自定义:根据imgs2poses.py生成sparse_points.ply和poses.npy文件,若先前没有经过colmap,则会生成sparse\0\*.bin文件,(cameras.bin, images.bin , points3D.bin)。然后根据gen_cameras.py文件,通过pose.npy读取第一个相机的c2w矩阵将第一个相机的单位坐标系保存为pose.ply文件,通过pose.npy和sparse_points_interest.ply文件生成preprocessed文件夹下的cameras_sphere.npz,并复制images生成image和mask文件夹下图片。
- imgs2poses.py
- sparse_points.ply:读取points3D文件中的所有点,生成的稀疏点云文件
- poses.npy:通过cameras.bin和images.bin文件计算出的pose数据:大小num_images x 3 x 5,包括num_images x 3 x 4的c2w矩阵和num_images x 3的hwf数据
- gen_cameras.py
- pose.ply:读取第一个相机的pose,将该相机坐标系下的原点、xyz轴单位坐标转换到世界坐标系下,然后生成点云保存为pose.ply文件
- cameras_sphere.npz
- world_mat:通过pose.npz读取pose矩阵,分解为c2w和hwf,并将c2w求逆得到w2c,将hwf转化为intrinsic相机内参矩阵,最后得到
world_mat=intrinsic @ w2c - scale_mat:通过sparse_points_interest.ply文件,将其中的感兴趣区域,在世界坐标系下计算出scale_mat,该矩阵用于将世界坐标系原点缩放并平移到感兴趣区域的中心处,使得世界坐标系下的单位圆即为感兴趣的区域,这也是不需要mask的原因
- image和mask:将images数据集文件夹下图片复制到preprocessed文件夹下的image下和并根据数据集图片生成同样大小的白色图片,放入mask文件夹
- world_mat:通过pose.npz读取pose矩阵,分解为c2w和hwf,并将c2w求逆得到w2c,将hwf转化为intrinsic相机内参矩阵,最后得到
数据处理:
- 读取cameras_sphere.npz文件、image和mask文件,获得相机的内外参矩阵intrinsics, pose,并对intrinsics求逆得到intrinsics_inv,在生成光线时用于将图片像素的坐标转换为光线在世界坐标系下的原点o和方向向量d。
- 通过o和d,生成场景中的near和far,即在每条光线上采样时,采样点的最近坐标和最远坐标
渲染:
- 根据o、d、near和far,以及其他参数,经过MLP网络,得到颜色值、sdf对输入pts_xyz的梯度等信息,然后计算loss,最后通过反向传播不断更新网络的参数,训练出最终的4个MLP网络
- 根据训练好的MLP网络,通过一个新相机点的位置,生成一系列光线,在光线上进行采样获得点云的坐标,然后将坐标输入MLP网络,获得三维空间中每个点云的颜色、SDF和梯度等信息。
- 颜色跟观察方向有关、SDF与方向无关、梯度与方向无关,颜色可以用来生成新视点的图片、视频,SDF可以用来根据threshold选取零水平集来生成mesh模型表面,梯度可以做法向量图。
dataset
self.dataset = Dataset(self.conf['dataset'])
- 相机内外参数矩阵
- 光线的生成以及坐标变换
BlendedMVS/bmvs_bear/cameras_sphere
1 | """ |
将P分解为相机内参和外参矩阵,in dataset.py
1 | out = cv.decomposeProjectionMatrix(P) |
光线生成
gen_random_rays_at()随机生成光线
然后生成光线,in dataset.py/gen_random_rays_at() by img_idx ,batch_size, 并将rays的像素坐标转换到世界坐标系下
p_pixel —> p_camera —> p_world (or rays_d)
p_camera = intrinsics_inv @ p_pixel: 3x3 @ 3x1
$\begin{bmatrix} \frac{1}{f} & 0 & -\frac{W}{2 \cdot f} \\ 0 & \frac{1}{f} & -\frac{H}{2 \cdot f} \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} i \\ j \\ 1 \\ \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} \frac{i-\frac{W}{2}}{f} \\ \frac{j-\frac{H}{2}}{f} \\ 1 \\ \end{pmatrix}$
p_world = pose @ p_camera: 3x3 @ 3x1
$\begin{bmatrix} r_{11}&r_{12}&r_{13}\\ r_{21}&r_{22}&r_{23}\\ r_{31}&r_{32}&r_{33} \end{bmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} x_{c} \\ y_{c} \\ z_{c} \\ \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} x_{w} \\ y_{w} \\ z_{w} \\ \end{pmatrix} = rays_d$
rays_o = pose[:3, 3] $= \begin{bmatrix} t_{x} \\ t_{y} \\ t_{z} \end{bmatrix}$,为相机坐标系原点在世界坐标系下位置
$pose = \begin{bmatrix}r_{11}&r_{12}&r_{13}&t_x\\ r_{21}&r_{22}&r_{23}&t_y\\ r_{31}&r_{32}&r_{33}&t_z\\ 0&0&0&1\end{bmatrix}$
1 | def gen_random_rays_at(self, img_idx, batch_size): |
计算near和far(from o,d)
根据rays_o 和rays_d 计算出near和far两个平面
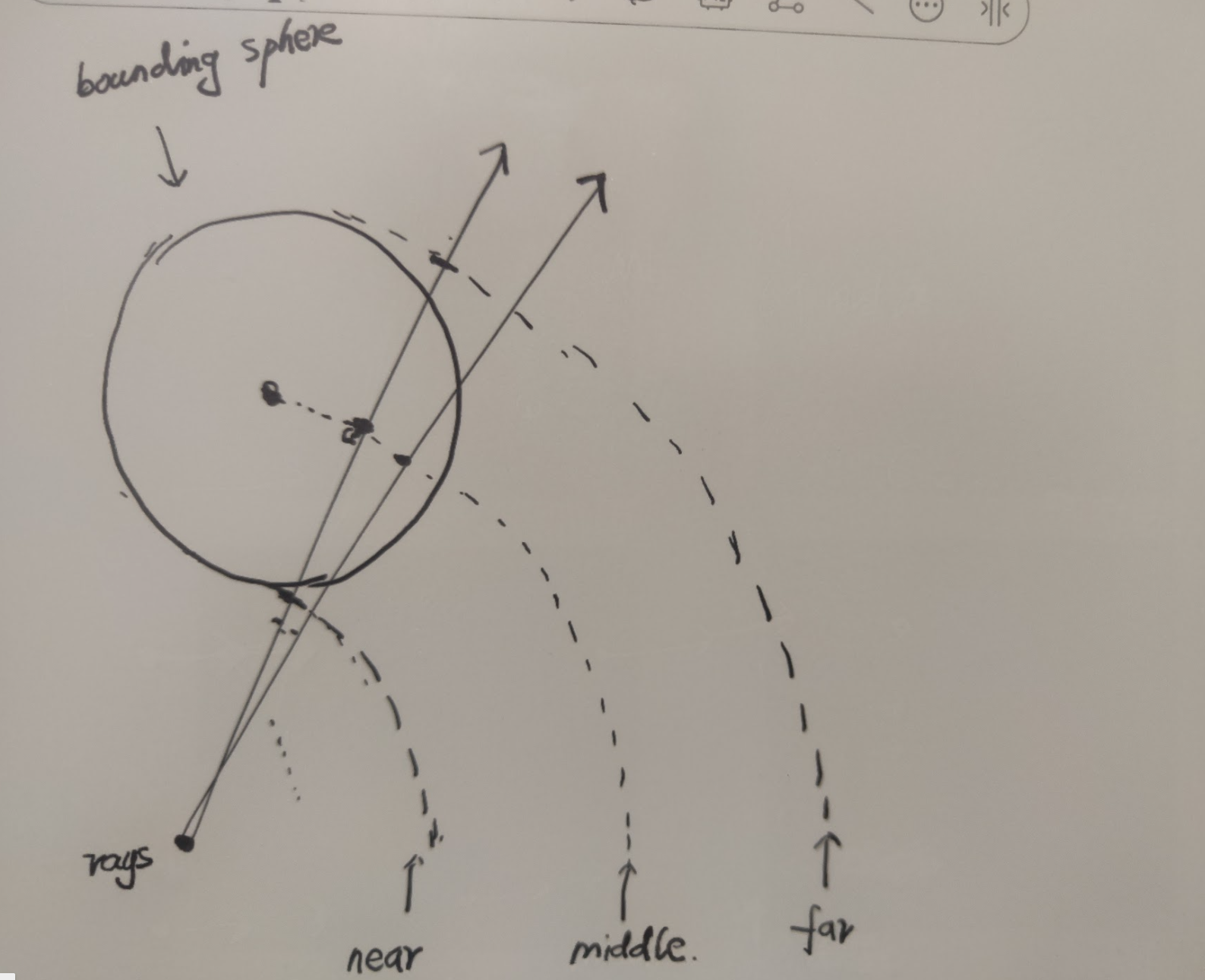
1 | def near_far_from_sphere(self, rays_o, rays_d): |
box的min和max(to生成mesh模型)
1 | ''' |
神经网络结构Network
1 | # Networks |
Neus中共构建了4个network:
- NeRF:训练物体outside即背景的颜色
- SDFNetwork:训练点云中的sdf值
- RenderingNetwork:训练点云的RGB
- SingleVarianceNetwork:训练一个单变量invs,用于计算$cdf = sigmoid(estimated.sdf \cdot inv.s)$
NeRF
同NeRF网络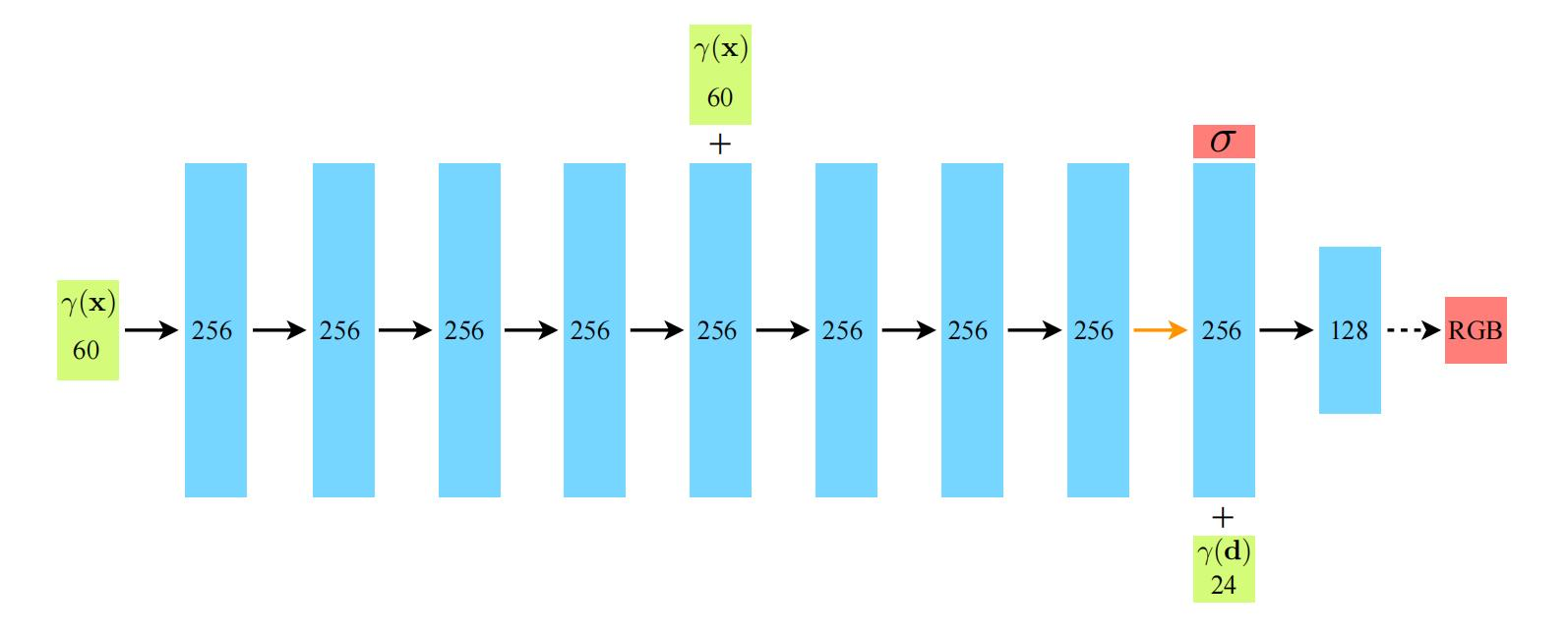
- 84—>256—>256—>256—>256—>256+84—>256—>256—>256+27—>128—>3
- 84—>256—>256—>256—>256—>256+84—>256—>256—>256—>1
SDFNetwork
激活函数 $\text{Softplus}(x) = \frac{\log(1 + e^{\beta x})}{\beta}$
网络结构: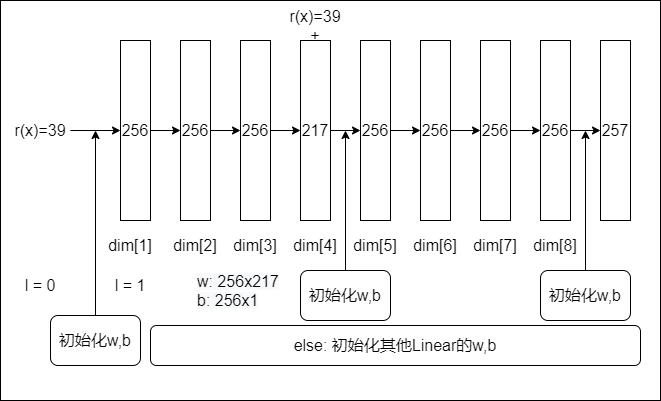
- 39—>256—>256—>256—>217—>256—>256—>256—>256—>257
input: pts, 采样点的三维坐标 batch_size n_samples x 3
output: 257个数 batch_size n_samples x 257
sdf(pts) = output[:, :1]: batch_size * n_samples x 1,采样点的sdf值
RenderingNetwork
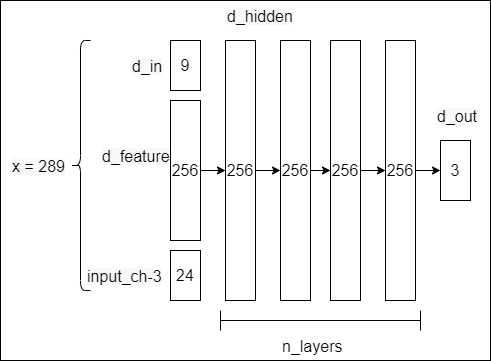
input: rendering_input :[batch_size * n_samples , 3 + 27 + 3+ 256 = 289]rendering_input = torch.cat([points, view_dirs, normals, feature_vectors], dim=-1)
- pts: batch_size * n_samples, 3
- gradients: batch_size * n_samples, 3
- dirs: batch_size * n_samples, 3
- 位置编码 to view_dirs: batch_size * n_samples , 27
- feature_vector: batch_size * n_samples, 256
output: sampled_color采样点的RGB颜色 batch_size * n_samples , 3
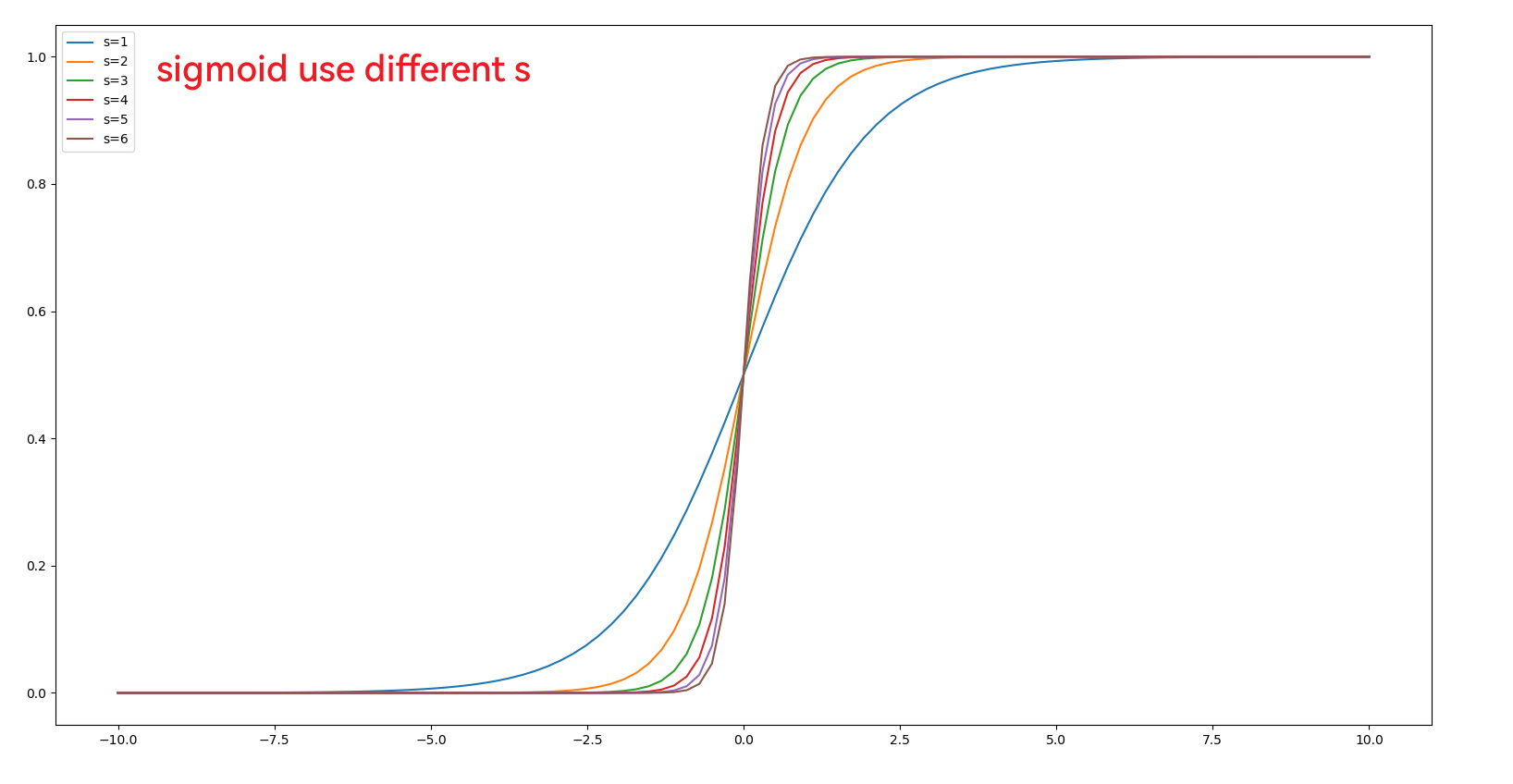
SingleVarianceNetwork
1 | class SingleVarianceNetwork(nn.Module): |
render中inv_s = deviation_network(torch.zeros([1, 3]))[:, :1].clip(1e-6, 1e6)
render
input:
- rays_o,
- rays_d, 单位向量
- near, far : batch_sizex1,batch_sizex1
- background_rgb=background_rgb,
- cos_anneal_ratio=self.get_cos_anneal_ratio()
1 | image_perm = self.get_image_perm() |
output: render_out字典
- color_fine: render出来图片的RGB颜色值
- s_val: $= \sum_{i}^{n.samples}(\frac{1.0}{invs_{i}})$
- inv_s: 一个可以更新的变量 $1 \times e^{10.0 \cdot var}$ ,并将其限制在$1 \times 10^{-6}$ ~ $1 \times 10^{6}$之间
ret_fine['s_val'] = 1.0 / inv_s# batch_size * n_samples, 1s_val = ret_fine['s_val'].reshape(batch_size, n_samples).mean(dim=-1, keepdim=True)# batch_size, 1
- cdf_fine: $pre.cdf = {\Phi_s(f(\mathbf{p}(t_i)))}$
- batch_size, n_samples
- weight_sum: 一条光线上的权重之和(包括背景outside)
- batch_size, 1
weights_sum = weights.sum(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
- weight_max: 一条光线上权重的最大值
- batch_size, 1
torch.max(weights, dim=-1, keepdim=True)[0]
- gradients: 梯度,sdf对输入pts_xyz的梯度,与法向量的计算有关
- batch_size, n_samples, 3
- weights: 权重,每个采样点
- batch_size, n_samples or batch_size, n_samples + n_outside
- gradient_error: Eikonal损失值$\mathcal{L}_{r e g}=\frac{1}{n m}\sum_{k,i}(|\nabla f(\hat{\mathbf{p}}_{k,i})|_{2}-1)^{2}.$ 只计算在relax半径为1.2的圆内的采样点sdf的梯度
- $|\nabla f(\hat{\mathbf{p}}_{k,i})|_{2} = \sqrt{gx^{2}+gy^{2}+gz^{2}}$
- inside_sphere: 采样点是否在单位圆空间内
- batch_size, n_samples
1 | { |
1 | ret_fine = self.render_core(rays_o, |
function:
1 | render: |
1 | 物体外的z坐标(背景) |
1 | 添加扰动: |
get_cos_anneal_ratio
output:
- 数1或者比一小的数$\frac{iterstep}{anneal}, anneal=50000$
- or 1 when anneal_end = 0
精采样n_importance
if self.n_importance > 0: 精采样
1 | with torch.no_grad(): # 不需要计算梯度 |
up_sample(self, rays_o, rays_d, z_vals, sdf, n_importance, inv_s):
input:
- rays_o,
- rays_d,
- z_vals, batch_size X n_samples
- sdf, batch_size X n_samples
- self.n_importance // self.up_sample_steps, 每步处理$\frac{importance}{sampls.steps}$
64 * 2**i, $64 \cdot 2^{i}$
output:
- new_z_vals: batch_size X n_importance // up_sample_steps * steps_i
function:
- pts: batch_size,n_samples,3
- radius: pts的2-范数norm(ord=2)
- batch_size, n_samples
- inside_sphere:
inside_sphere = (radius[:, :-1] < 1.0) | (radius[:, 1:] < 1.0)- point是否在单位圆的空间内
- batch_size, n_samples - 1
- prev_sdf, next_sdf: 光线上sdf的前后
prev_sdf[1] = next_sdf[0] = sdf[1]- batch_size, n_samples - 1
- prev_z_vals, next_z_vals: 光线上z坐标的前后
prev_z_vals[1] = next_z_vals[0] = z_vals[1]- batch_size, n_samples - 1
- mid.sdf: $mid.sdf = \frac{prev.sdf + next.sdf}{2} = \frac{f(p_{i})+f(p_{i+1})}{2}$
- batch_size, n_samples - 1
cos_val: $cos.val = \frac{next.sdf - prev.sdf}{next.z.vals - prev.z.vals + 1e-5} = \frac{f(p_{i})-f(p_{i+1})}{z_{i}-z_{i+1}}$
- batch_size, n_samples - 1
prev_cos_val: 将cos_val堆叠,且最后一个删除,第一个插入0
prev_cos_val[0] = 0, prev_cos_val[1] = cos_val[0]- batch_size, n_samples - 1
- cos_val: stack prev_cos_val and cos_val
- batch_size, n_samples - 1, 2
- cos_val: 在prev_cos_val和cos_val之间选择最小值,这一步的目的是当发生一条光线穿过物体两次时,具有更好的鲁棒性
- batch_size, n_samples - 1
- cos_val: 将cos_val限制在$-1 \times 10^{3}$和0之间,并将在单位圆空间外的值置False
cos_val.clip(-1e3, 0.0) * inside_sphere- batch_size, n_samples - 1
- dist: 两点之间的距离 $dist = next.z.vals- prev.z.vals= z_{i+1}-z_{i}$
- batch_size, n_samples - 1
batch_size, n_samples - 1:
- prev_esti_sdf: $\frac{mid.sdf - cos.val * dist}{2} \approx f(p_{i})$
- next_esti_sdf: $\frac{mid.sdf + cos.val * dist}{2} \approx f(p_{i+1})$
- prev_cdf: $prev.cdf = sigmoid(prev.esti.sdf \times inv.s) = sigmoid(\approx f(p_{i})\times 64 \cdot 2^{i})$
- next_cdf: $next.cdf = sigmoid(next.esti.sdf \times inv.s) = sigmoid(\approx f(p_{i+1})\times 64 \cdot 2^{i})$
- alpha: $\alpha = \frac{prev.cdf - next.cdf + 1 \times 10^{-5}}{prev.cdf + 1 \times 10^{-5}}$ is $\alpha_i=\max\left(\frac{\Phi_s(f(\mathbf{p}(t_i))))-\Phi_s(f(\mathbf{p}(t_{i+1})))}{\Phi_s(f(\mathbf{p}(t_i)))},0\right).$
- weights: $w_{i} = \alpha_{i} \cdot T_{i} =\alpha_{i} \cdot \prod_{j=1}^{i-1}(1-\alpha_j)$
- in code :
weights = alpha * torch.cumprod(torch.cat([torch.ones([batch_size, 1]), 1. - alpha + 1e-7], -1), -1)[:, :-1]
- in code :
z_samples = sample_pdf(z_vals, weights, n_importance, det=True).detach()
sample_pdf(z_vals, weights, n_importance, det=True)
like NeRF
input:
- z_vals, batch_size X n_samples
- weights, batch_size, n_samples - 1
- n_importance,
- det=True
output:
- z_samples, batch_size X n_importance 经过逆变换采样得到的采样点的z坐标值
cat_z_vals(rays_o,rays_d,z_vals,new_z_vals,sdf,last=(i + 1 == self.up_sample_steps))
将原来的z_vals和经过逆变换采样得到的new_z_vals一起cat起来
input:
- rays_o,
- rays_d,
- z_vals, batch_size X n_samples
- new_z_vals,
batch_size X n_importance // up_sample_steps * steps_i - sdf, batch_size X n_samples
- last=(i + 1 == self.up_sample_steps): true(last step) or false
output:
- z_vals,
batch_size X n_samples + n_importance // up_sample_steps * steps_i - sdf,
batch_size X n_samples + n_importance // up_sample_steps * steps_iwhen not last
last:1
2z_vals : batch_size X n_samples + n_importance
n_samples = self.n_samples + self.n_important
then :
- z_vals : batch_size X n_samples
render_core_outside(rays_o, rays_d, z_vals_feed, sample_dist, self.nerf)
1 | in render() |
input:
- rays_o,
[batch_size, 3] - rays_d,
[batch_size, 3] - z_vals_feed,
batch_size, n_samples + n_outside,实际上此处为[batch_size, n_samples + n_outside +n_importance] - sample_dist, $sample.dist = \frac{2.0}{n.samples}$
- self.nerf, NeRF神经网络,使用nerf渲染函数进行color的计算
- 如果使用了白色背景,color还需累加白背景
background_rgb = torch.ones([1, 3])color = color + background_rgb * (1.0 - weights_sum)
- 如果使用了白色背景,color还需累加白背景
output: ret_outside字典1
2
3
4
5
6{
'color': color, # batch_size, 3
'sampled_color': sampled_color, # batch_size, n_samples + n_outside, 3
'alpha': alpha, # batch_size, n_samples + n_outside
'weights': weights, # batch_size, n_samples + n_outside
}
function: like NeRF
- dis_to_center: 坐标的2范数,并限制在$1$ ~ $1 \times 10^{10}$
- batch_size, n_samples, 1
- pts:
torch.cat([pts / dis_to_center, 1.0 / dis_to_center], dim=-1)- batch_size, n_samples, 4
- 归一化pts, $\frac{x}{\sqrt{x^{2}+y^{2}+z^{2}}},\frac{y}{\sqrt{x^{2}+y^{2}+z^{2}}},\frac{z}{\sqrt{x^{2}+y^{2}+z^{2}}},\frac{1}{\sqrt{x^{2}+y^{2}+z^{2}}}$
render_core()
1 | render continue |
input:
- rays_o,
[batch_size, 3] - rays_d,
[batch_size, 3] - z_vals,
batch_size, n_samples,实际上为batch_size, n_samples + n_importance - sample_dist, $sample.dist = \frac{2.0}{n.samples}$
- self.sdf_network, sdf神经网络
- self.deviation_network, inv_s参数神经网络
- self.color_network, 采样点color神经网络
- background_rgb=background_rgb,
batch_size, 3 - background_alpha=background_alpha,
batch_size, n_samples + n_outside - background_sampled_color=background_sampled_color,
batch_size, n_samples + n_outside, 3 - cos_anneal_ratio=cos_anneal_ratio ,数1或者比一小的数$\frac{iterstep}{anneal}, anneal=50000$
output: ret_fine字典1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12{
'color': color, # batch_size, 3
'sdf': sdf, # batch_size * n_samples, 1
'dists': dists, # batch_size, n_samples
'gradients': gradients.reshape(batch_size, n_samples, 3),
's_val': 1.0 / inv_s, # batch_size * n_samples, 1
'mid_z_vals': mid_z_vals, # batch_size, n_samples
'weights': weights, # batch_size, n_samples or batch_size, n_samples + n_outside
'cdf': c.reshape(batch_size, n_samples), # batch_size, n_samples
'gradient_error': gradient_error, # 1
'inside_sphere': inside_sphere # batch_size, n_samples
}
function:
- dists: 采样点间距离,$dists = z_{i+1} - z_{i}$
- batch_size, n_samples - 1
- dists: 最后一行添加固定的粗采样点间距: $sample.dist = \frac{2.0}{n.samples}$
- batch_size, n_samples
- mid_z_vals: $mid = z_{i} + \frac{dist_{i}}{2}$
- batch_size, n_samples
- pts: $pts = \vec o + \vec d \cdot mid$
- batch_size, n_samples, 3
- dirs: 方向向量扩展得到
rays_d[:, None, :].expand(batch_size, n_samples, 3)- batch_size, n_samples, 3
- pts: reshape to batch_size * n_samples, 3
- dirs: reshape to batch_size * n_samples, 3
- sdf_nn_output: = sdf_network(pts)
- batch_size * n_samples, 257
- sdf:
sdf = sdf_nn_output[:, :1]- batch_size * n_samples, 1
- feature_vector:
feature_vector = sdf_nn_output[:, 1:]- batch_size * n_samples, 256
- gradients: 梯度,sdf对输入pts_xyz的梯度,与法向量有关
- batch_size * n_samples, 3
1 | def gradient(self, x): |
- sampled_color: batch_size, n_samples, 3
color_network(pts, gradients, dirs, feature_vector).reshape(batch_size, n_samples, 3)
- inv_s:
deviation_network(torch.zeros([1, 3]))[:, :1].clip(1e-6, 1e6)- 一个可以更新的变量 $1 \times e^{10.0 \cdot var}$ ,并将其限制在$1 \times 10^{-6}$ ~ $1 \times 10^{6}$之间
- 这个变量是用于sigmoid函数的输入,使其乘以s
1 | class SingleVarianceNetwork(nn.Module): |
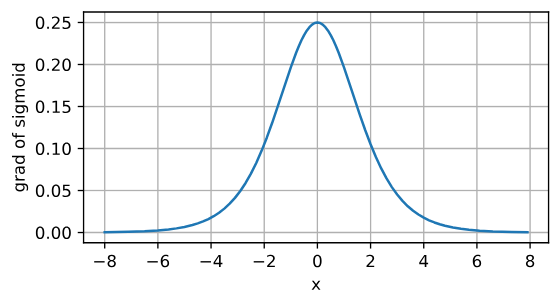
可以看出sigmoid函数的导数是一个偶函数,即$\phi(-x) = \phi(x)$
- inv_s: expand a num to
batch_size * n_samples, 1 - true_cos: $true.cos = \frac{dx \cdot gx + dy \cdot gy + dz \cdot gz}{\sqrt{dx^{2}+dy^{2}+dz^{2}} \cdot \sqrt{gx^{2}+gy^{2}+gz^{2}}}$ 为sdf梯度方向,即物体表面的法线方向向量$\vec g$与光线方向向量$\vec d$的夹角
- batch_size * n_samples, 1
true_cos = (dirs * gradients).sum(-1, keepdim=True)
why true_cos = (dirs * gradients).sum(-1, keepdim=True)
- cdf对t的导数:$\frac{\mathrm{d}\Phi_s}{\mathrm{d}t}(f(\mathbf{p}(t)))= \nabla f(\mathbf{p}(t))\cdot\mathbf{v} \cdot \phi_s(f(\mathbf{p}(t)))$
- sdf对t的导数:$\frac{\mathrm{d}f(\mathbf{p}(t))}{\mathrm{d}t}= \nabla f(\mathbf{p}(t))\cdot\mathbf{v}$,即为true_cos
- iter_cos: $= -[relu(\frac{-true.cos+1}{2}) \cdot (1.0 - cos.anneal.ratio)+ relu(-true.cos) \cdot cos.anneal.ratio]$
- batch_size * n_samples, 1
- iter_cos 总是非正数
- cos_anneal_ratio 数1或者比一小的数$\frac{iterstep}{anneal}, anneal=50000$ in womask cos_anneal_ratio is from 0 to 1, and always 1 after anneal steps
- anneal = 0 in wmask, then cos_anneal_ratio is always 1
batch_size * n_samples, 1:
- estimated_next_sdf: $est.next.sdf = sdf + iter.cos \times dist \times 0.5$
estimated_next_sdf = sdf + iter_cos * dists.reshape(-1, 1) * 0.5
- estimated_prev_sdf: $est.prev.sdf = sdf - iter.cos \times dist \times 0.5$
estimated_prev_sdf = sdf - iter_cos * dists.reshape(-1, 1) * 0.5
- prev_cdf: $prev.cdf = sigmoid(est.prev.sdf \cdot inv.s)$
prev_cdf = torch.sigmoid(estimated_prev_sdf * inv_s)
- next_cdf: $next.cdf = sigmoid(est.next.sdf \cdot inv.s)$
next_cdf = torch.sigmoid(estimated_next_sdf * inv_s)
p = prev_cdf - next_cdf , c = prev_cdfalpha: $\alpha = \frac{p + 10^{-5}}{c + 10^{-5}} = \frac{prev.cdf - next.cdf}{prev.cdf}$ and in (0.0,1.0)
- batch_size, n_samples
alpha = ((p + 1e-5) / (c + 1e-5)).reshape(batch_size, n_samples).clip(0.0, 1.0)
- pts_norm: $\sqrt{x^{2}+y^{2}+z^{2}}$
- batch_size, n_samples
pts_norm = torch.linalg.norm(pts, ord=2, dim=-1, keepdim=True).reshape(batch_size, n_samples)
- inside_sphere, 在单位圆内的点置位 True,在外的为False
- batch_size, n_samples
inside_sphere = (pts_norm < 1.0).float().detach()
- relax_inside_sphere,更放松一点的限制:在半径1.2的圆内的点
- batch_size, n_samples
relax_inside_sphere = (pts_norm < 1.2).float().detach()
if background_alpha 不是 None,计算过背景的alpha值,将背景与物体前景的alpha和采样点颜色值cat起来
1 | if background_alpha is not None: |
- weights,计算每个采样点的权重 $w_{i} = \alpha_{i} \cdot T_{i} =\alpha_{i} \cdot \prod_{j=1}^{i-1}(1-\alpha_j)$
- batch_size, n_samples or batch_size, n_samples + n_outside
weights = alpha * torch.cumprod(torch.cat([torch.ones([batch_size, 1]), 1. - alpha + 1e-7], -1), -1)[:, :-1]
- weights_sum:权重的和,方便前景颜色与背景的颜色进行累加
- batch_size, 1
weights_sum = weights.sum(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
- color:$\hat{C}=\sum_{i=1}^n T_i\alpha_i c_i,$
- batch_size, 3
- `color = (sampled_color * weights[:, :, None]).sum(dim=1)
累加背景的颜色值
1 | if background_rgb is not None: # Fixed background, usually black |
计算loss
$\mathcal{L}_{r e g}=\frac{1}{n m}\sum_{k,i}(|\nabla f(\hat{\mathbf{p}}_{k,i})|_{2}-1)^{2}.$ 只计算在relax半径为1.2的圆内的采样点sdf的梯度
$|\nabla f(\hat{\mathbf{p}}_{k,i})|_{2} = \sqrt{gx^{2}+gy^{2}+gz^{2}}$
1 | # Eikonal loss |
render后
get loss
- color_fine_loss: $\mathcal{L}_{color}=\frac{1}{m}\sum_k\mathcal{R}(\hat{C}_k,C_k).$
- eikonal_loss: $\mathcal{L}_{r e g}=\frac{1}{n m}\sum_{k,i}(|\nabla f(\hat{\mathbf{p}}_{k,i})|_{2}-1)^{2}.$
- mask_loss: $\mathcal{L}_{mask}=\mathrm{BCE}(M_k,\hat{O}_k)$
total loss: $\mathcal L=\mathcal L_{color}+\lambda\mathcal L_{reg}+\beta\mathcal L_{mask}.$
- igr_weight = 0.1
- mask_weight = 0.1 or 0.0 if womask
1 | color_error = (color_fine - true_rgb) * mask |
backward
1 | self.optimizer.zero_grad() |
log(tensorboard.scalar)
1 | from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter |
other per step
1 | if self.iter_step % self.report_freq == 0: |
validate_image
将图片缩小resolution_level倍进行光线生成,然后分批次进行渲染,每批大小为batch_size
1 | def validate_image(self, idx=-1, resolution_level=-1): |
最终得到该图片每个像素的颜色值out_rgb_fine,以及inside_sphere内的法向量值out_normal_fine
1 | for rays_o_batch, rays_d_batch in zip(rays_o, rays_d): |
然后进行图片的拼接和保存

.png)
1 | img_fine = None |
validate_mesh生成mesh模型
根据一个$resolution^3$ 的sdf场,将阈值为0的点使用marching_cubes方法生成vertices和triangles,然后生成mesh的ply文件
extract_geometry
extract_fields
input:
- bound_min : 3 ; bound_max : 3 ; resolution : 64
- query_func : pts -> sdf
output: u
u : resolution x resolution x resolution, 为box 中每个点的sdf值
extract_geometry
根据体积数据和阈值重建出表面
pmneila/PyMCubes: Marching cubes (and related tools) for Python (github.com)
input:
- bound_min, bound_max, resolution,
- threshold, 用于
vertices, triangles = mcubes.marching_cubes(u, threshold),在等threshold面上,生成mesh的v和t - query_func,根据位置pts利用network计算出sdf
- query_func=lambda pts: -self.sdf_network.sdf(pts)
output:
- query_func=lambda pts: -self.sdf_network.sdf(pts)
- vertices:三角形网格点
- N_v , 3: 3为点的三维坐标
- triangles:三角形网格
- N_t , 3: 3为三角形网格顶点的索引index
根据v和t,mesh = trimesh.Trimesh(vertices, triangles)生成mesh,并导出ply:1
mesh.export(os.path.join(self.base_exp_dir, 'meshes', '{:0>8d}.ply'.format(self.iter_step)))
数据集自定义
custom_data流程图
imgs2poses.py
是否使用过colmap:
- 如果已经使用colmap生成了
sparse/0/下的['cameras', 'images', 'points3D']文件,将获得sparse_points.ply - 若没有,则使用
run_colmap(),即可生成sparse/0/下文件
run_colmap()
1 | def run_colmap(basedir, match_type): |
上述代码相当于分别运行:1
2
3
4colmap feature_extractor --database_path os.path.join(basedir, 'database.db') --image_path os.path.join(basedir, 'images') --ImageReader.single_camera 1
colmap match_type --database_path os.path.join(basedir, 'database.db')
match_type : exhaustive_matcher Or sequential_matcher
colmap mapper --database_path os.path.join(basedir, 'database.db') --image_path os.path.join(basedir, 'images') --output_path os.path.join(basedir, 'sparse') --Mapper.num_threads 16 --Mapper.init_min_tri_angle 4 --Mapper.multiple_models 0 --Mapper.extract_colors 0
- feature_extractor: Perform feature extraction or import features for a set of images.
- exhaustive_matcher: Perform feature matching after performing feature extraction.
- mapper: Sparse 3D reconstruction / mapping of the dataset using SfM after performing feature extraction and matching.
然后将命令行的输出结果保存到logfile即basedir/colmap_output.txt中
colmap命令行:Command-line Interface — COLMAP 3.8-dev documentation
dense中深度图转换:COLMAP简明教程 导入指定参数 命令行 导出深度图 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
load_colmap_data() to colmap_read_model.py
python .\colmap_read_model.py E:\BaiduSyncdisk\NeRF_Proj\NeuS\video2bmvs\M590\sparse\0 .bin
读取['cameras', 'images', 'points3D']文件的数据
input:
- basedir
output:
- poses, shape: 3 x 5 x num_images
- c2w: 3x4xn
- hwf: 3x1xn
- pts3d, 一个长度为num_points字典,key为point3D_id,value为Point3D对象
- perm, # 按照name排序,返回排序后的索引的列表:
[from 0 to num_images-1]
cameras images and pts3d be like:
| var | example | info |
|---|---|---|
| cameras | {1: Camera(id=1, model='SIMPLE_RADIAL', width=960, height=544, params=array([ 5.07683492e+02, 4.80000000e+02, 2.72000000e+02, -5.37403479e-03])), ...} |
f, cx, cy, k=params |
| images | {1: Image(id=1, qvec=array([ 0.8999159 , -0.29030237, 0.07162026, 0.31740581]), tvec=array([ 0.29762954, -2.81576928, 1.41888716]), camera_id=1, name='000.png', xys=xys, point3D_ids=point3D_ids, ...} |
perm = np.argsort(names),qvec,tvec to m=w2c_mats:4x4, |
| pts3D | {1054: Point3D(id=1054, xyz=array([1.03491375, 1.65809594, 3.83718124]), rgb=array([147, 146, 137]), error=array(0.57352093), image_ids=array([115, 116, 117, 114, 113, 112]), point2D_idxs=array([998, 822, 912, 977, 889, 817])), ...} |
xys and point3D_ids in images be like:
1 | xys=array([[ 83.70032501, 2.57579875], |
cameras文件
input:
- path_to_model_file,
camerasfile = os.path.join(realdir, 'sparse/0/cameras.bin')
output: - cameras,一个长度为num_cameras字典,key为camera_id,value为Camera对象
使用:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9camerasfile = os.path.join(realdir, 'sparse/0/cameras.bin')
camdata = read_model.read_cameras_binary(camerasfile)
list_of_keys = list(camdata.keys()) # list from 1 to num_cameras
cam = camdata[list_of_keys[0]] # Camera(id=1, model='SIMPLE_RADIAL', width=960, height=544, params=array([ 5.07683492e+02, 4.80000000e+02, 2.72000000e+02, -5.37403479e-03]))
print( 'Cameras', len(cam)) # Cameras 5
h, w, f = cam.height, cam.width, cam.params[0]
hwf = np.array([h,w,f]).reshape([3,1])
images文件
input:
- path_to_model_file,
imagesfile = os.path.join(realdir, 'sparse/0/images.bin')
output: - images,一个长度为num_reg_images字典,key为image_id,value为Image对象
使用:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26imagesfile = os.path.join(realdir, 'sparse/0/images.bin')
imdata = read_model.read_images_binary(imagesfile)
w2c_mats = []
bottom = np.array([0,0,0,1.]).reshape([1,4])
names = [imdata[k].name for k in imdata] # 一个长度为num_images的list,每个元素为图片的名字
print( 'Images #', len(names))
perm = np.argsort(names) # 按照name排序,返回排序后的索引的列表:[from 0 to num_images-1]
for k in imdata:
im = imdata[k]
R = im.qvec2rotmat() # 将旋转向量转换成旋转矩阵 3x3
t = im.tvec.reshape([3,1]) # 平移向量 3x1
m = np.concatenate([np.concatenate([R, t], 1), bottom], 0) # 4x4
w2c_mats.append(m) # 一个长度为num_images的list,每个元素为4x4的矩阵
w2c_mats = np.stack(w2c_mats, 0) # num_images x 4 x 4
c2w_mats = np.linalg.inv(w2c_mats) # num_images x 4 x 4
poses = c2w_mats[:, :3, :4].transpose([1,2,0]) # 3 x 4 x num_images
poses = np.concatenate([poses, np.tile(hwf[..., np.newaxis], [1,1,poses.shape[-1]])], 1)
# tile : 将hwf扩展成3 x 1 x 1 ,然后tile成3 x 1 x num_images,tile表示在某个维度上重复多少次
# poses : 3 x 5 x num_images ,c2w:3 x 4 x num_images and hwf: 3 x 1 x num_images
# must switch to [-u, r, -t] from [r, -u, t], NOT [r, u, -t]
poses = np.concatenate([poses[:, 1:2, :], poses[:, 0:1, :], -poses[:, 2:3, :], poses[:, 3:4, :], poses[:, 4:5, :]], 1)
其中R = im.qvec2rotmat()将旋转向量转换成旋转矩阵:
如果给定旋转向量为 [qw, qx, qy, qz],其中 qw 是标量部分,qx, qy, qz 是向量部分,可以通过以下步骤将旋转向量转换为旋转矩阵:
构造单位四元数 q:1
q = qw + qx * i + qy * j + qz * k 其中 i, j, k 是虚部的基本单位向量。
计算旋转矩阵 R(w2c):1
2
3R = | 1 - 2*(qy^2 + qz^2) 2*(qx*qy - qw*qz) 2*(qx*qz + qw*qy) |
| 2*(qx*qy + qw*qz) 1 - 2*(qx^2 + qz^2) 2*(qy*qz - qw*qx) |
| 2*(qx*qz - qw*qy) 2*(qy*qz + qw*qx) 1 - 2*(qx^2 + qy^2) |
1 | def qvec2rotmat(qvec): |
points3D文件
input:
- path_to_model_file:
points3dfile = os.path.join(realdir, 'sparse/0/points3D.bin')
output: - pts3D, 一个长度为num_points字典,key为point3D_id,value为Point3D对象
1 | points3dfile = os.path.join(realdir, 'sparse/0/points3D.bin') |
save_poses.py
input:
- basedir,
- poses, shape: 3 x 5 x num_images
- c2w: 3x4xn
- hwf: 3x1xn
- pts3d, 一个长度为num_points字典,key为point3D_id,value为Point3D对象
{1054: Point3D(id=1054, xyz=array([1.03491375, 1.65809594, 3.83718124]), rgb=array([147, 146, 137]), error=array(0.57352093), image_ids=array([115, 116, 117, 114, 113, 112]), point2D_idxs=array([998, 822, 912, 977, 889, 817])), ...}
- perm, # 按照name排序,返回排序后的索引的列表:
[from 0 to num_images-1]
save:
- sparse_points.ply :
- pcd = trimesh.PointCloud(pts) , pts: num_points x 3
- poses.npy : num_images x 3 x 5
1 | def save_poses(basedir, poses, pts3d, perm): |
gen_cameras.py
根据pose.npy文件和sparse_points_interest.ply文件来生成cameras_sphere.npz
- pose.npy主要保存每张图片的c2w矩阵和hwf
- sparse_points_interest.ply用来生成相机缩放矩阵,将感兴趣的部位保存下来
pose文件
pose.ply in Miku
1 | work_dir = sys.argv[1] |
两个矩阵
world_mat_{i}:
1 | h, w, f = hwf[i, 0], hwf[i, 1], hwf[i, 2] |
pose要乘以covert_mat是因为在load_colmap_data时对pose进行了翻转
1 | # must switch to [-u, r, -t] from [r, -u, t], NOT [r, u, -t] |
scale_mat_{i}:
1 | pcd = trimesh.load(os.path.join(work_dir, 'sparse_points_interest.ply')) |
interpolate_view
生成一个视频,从img_idx_0中间插值生成新视图的图片,过渡到img_idx_1,然后再回到img_idx_0,共2s,60frames
eg: 0 to 38 render video

插值:$ratio = \frac{\sin{\left(\frac{i}{frames}-0.5 \right)\cdot \pi}}{2}+\frac{1}{2} = 0.5 \rightarrow 1 \rightarrow 0.5$
1 | def interpolate_view(self, img_idx_0, img_idx_1): |
1 | def render_novel_image(self, idx_0, idx_1, ratio, resolution_level): |
1 | def gen_rays_between(self, idx_0, idx_1, ratio, resolution_level=1): |