Uncertainty in everything
“Uncertainty quantification involves several key steps, which include data collection, mathematical modeling, uncertainty propagation, identifying critical outcomes, and making decisions under uncertainty.” (Faes 等, 2025, p. 14) (pdf)
Uncertainty
Uncertainty来源:
- 参数不确定性:缺乏知识(尤其是针对复杂的结构系统、新型复合材料、非线性动力学系统…)
- 模型形式不确定性:非线性特性的线性化、复杂连接关系用简单单元代替
- 试验不确定性:实验中难以控制的随机性,例如环境噪声、系统误差,主观判断…
Uncertainty分类:
- Epistemic Uncertainty源自认知信息不足,可以减少乃至消除
- Aleatory Uncertainty源自系统/结构固有的随机性
根据参数中是否存在Epistemic Uncertainty/Aleatory Uncertainty,将参数分为四类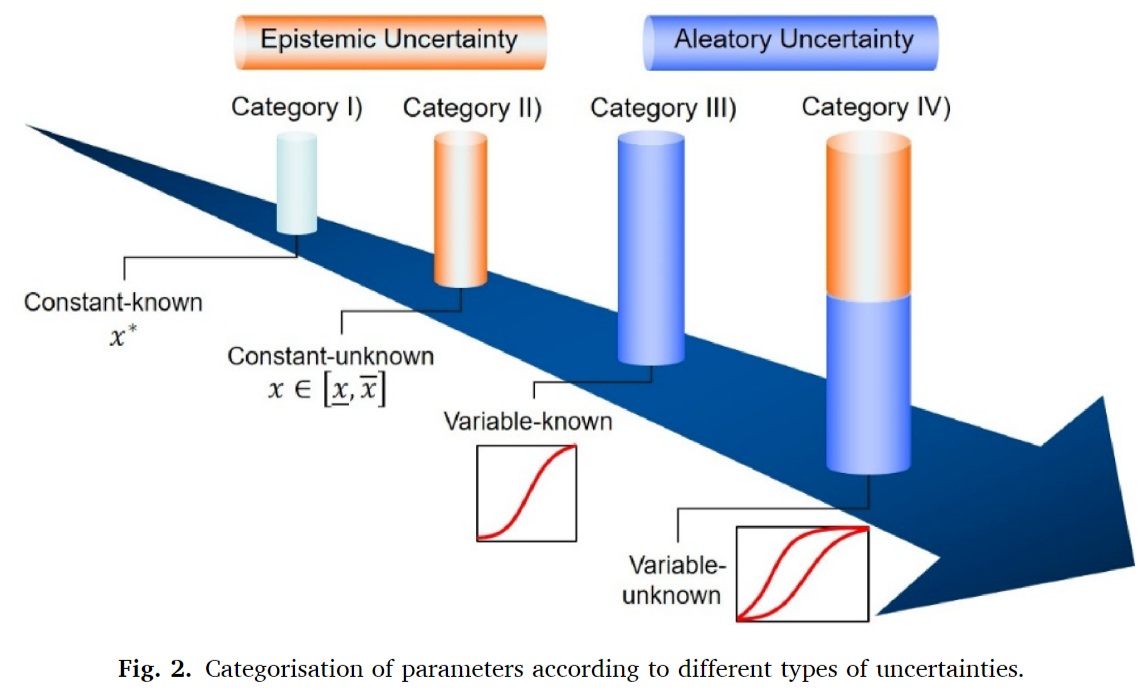
- Category 1:具有完全确定值的常数
- Category 2:未知但固定的常数(区间)
- Category 3:具有完全确定分布性质的随机变量(分布格式、均值和方差),称为精确概率
- Category 4:随机变量,分布性质尚未完全确定,称为不精确概率,可以通过P-box来建模,P-box中无限数量的CDF曲线构成了概率空间中的特定区域
确定模型修正适用于Category 2参数,确定预定义区间内的特定值
随机模型修正适用于Category 2~4类参数,可以通过
- 减少二类和四类参数的认知不确定性
- 合适地特征化三类参数的随机不确定性
浅谈Epistemic Uncertainty 和 Aleatoric Uncertainty - 知乎
【实验笔记】深度学习中的两种不确定性(上) - 知乎
不确定性根据系统内的不确定性来源可以分为Aleatoric Uncertainty和Epistemic Uncertainty,Aleatoric Uncertainty通常指的是数据不确定性,往往来自于数据本身的randomness或variability,是数据固有的一种属性。Epistemic uncertainty通常指的是模型不确定性或认知不确定性,其不确定性通常来源于缺乏足量信息的支撑。
Stochastic Model Updating with Uncertainty Quantification: An Overview and Tutorial - ScienceDirect
Uncertainty sources:Parameter uncertainty、Model form uncertainty、Experiment uncertainty
根据参数是否存在认知epistemic和/或选择性(偶然)aleatory不确定性,将不确定性参数分为四类:
- 既不具有认知不确定性,也不具有选择性不确定性的参数被表示为具有完全确定值的常数。
- 只有认知不确定性的参数被表示为一个未知但固定的常数,落在预定义的区间内。
- 将仅具有aleatory偶然不确定性的参数表示为具有完全确定的分布性质(如分布格式、均值、方差等)的随机变量。这种完全确定的分布称为“精确概率”。
- 同时具有认知不确定性和选择性不确定性的参数被表示为一个分布性质不完全确定的随机变量,即“不精确概率”。这种不精确的概率由所谓的概率盒(P-box)来建模,其中无限数量的累积分布函数(CDF)曲线构成概率空间中的特定区域。
Aleatory or epistemic? Does it matter? - ScienceDirect Structural Safety
Uncertainty is categorized
- Epistemic: the modeler sees a possibility to reduce them by gathering more data or by refining models. 可以减少
- Aleatory: the modeler does not foresee the possibility of reducing them. 无法减少
A Survey of Uncertainty in Deep Neural Networks
Gawlikowski et al., A Survey of Uncertainty in Deep Neural Networks, 2022-01-18
Uncertainty factors in DNN:
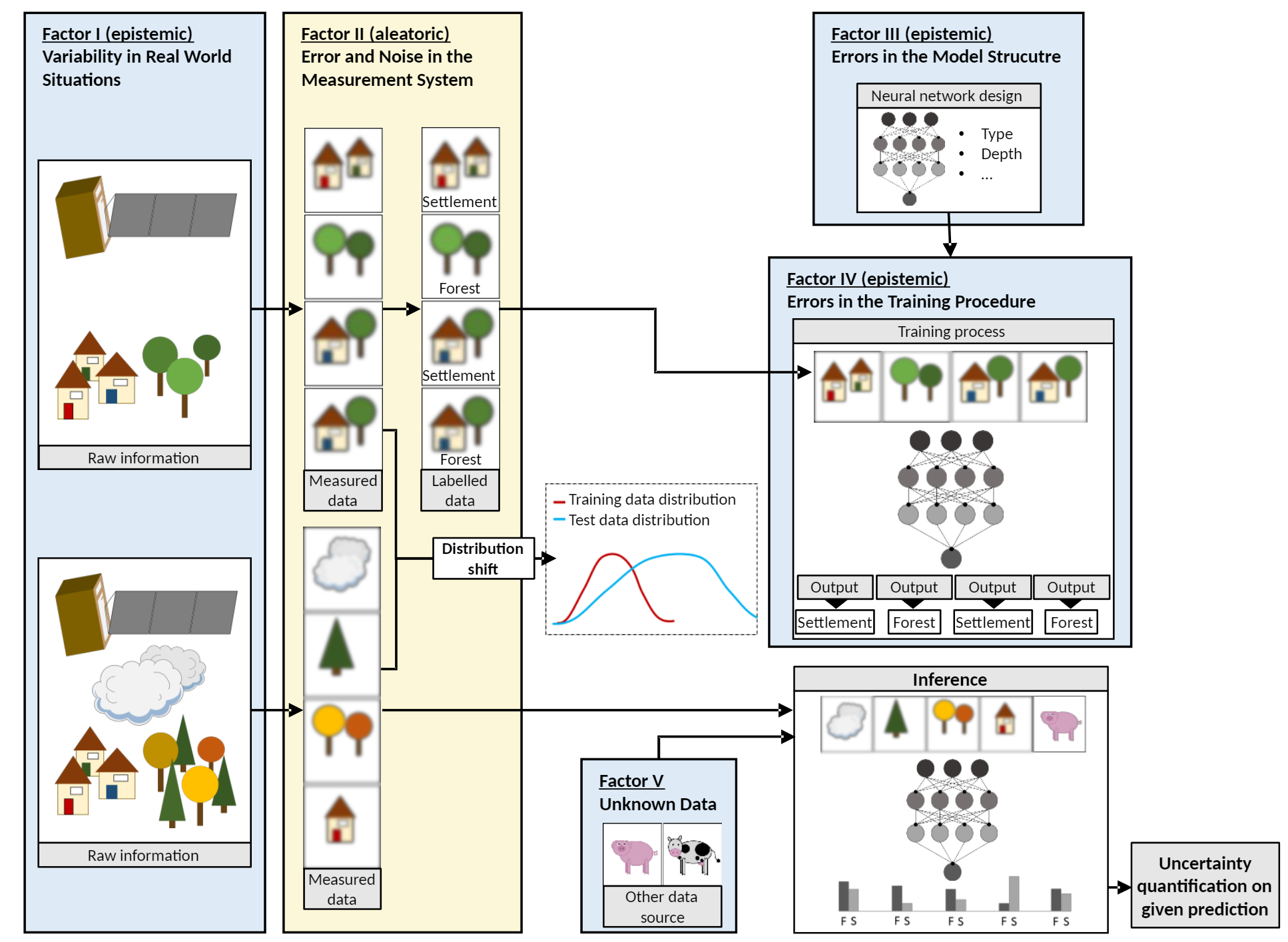
- “Factor I: Variability in Real World Situations” (Gawlikowski 等, 2022, p. 3) (pdf)
- “Factor II: Error and Noise in Measurement Systems” (Gawlikowski 等, 2022, p. 3) (pdf)
- “Factor III: Errors in the Model Structure” (Gawlikowski 等, 2022, p. 3) (pdf)
- “Factor IV: Errors in the Training Procedure” (Gawlikowski 等, 2022, p. 4) (pdf)
- “Factor V: Errors Caused by Unknown Data” (Gawlikowski 等, 2022, p. 4) (pdf)
Predictive Uncertainty Model:由于神经网络的预测主要收到模型和数据误差的影响,因此预测不确定性通常被分为 model uncertainty (both aleatory and epistemic) 和 data uncertainty (both aleatory and epistemic),此外还有distributional uncertainty 主要由样本没有被训练data覆盖导致。
- model uncertainty:caused by shortcomings in the model, either by errors in the training procedure, an insufficient model structure, or lack of knowledge due to unknown samples or a bad coverage of the training data set.
- data uncertainty:directly stems from the data.
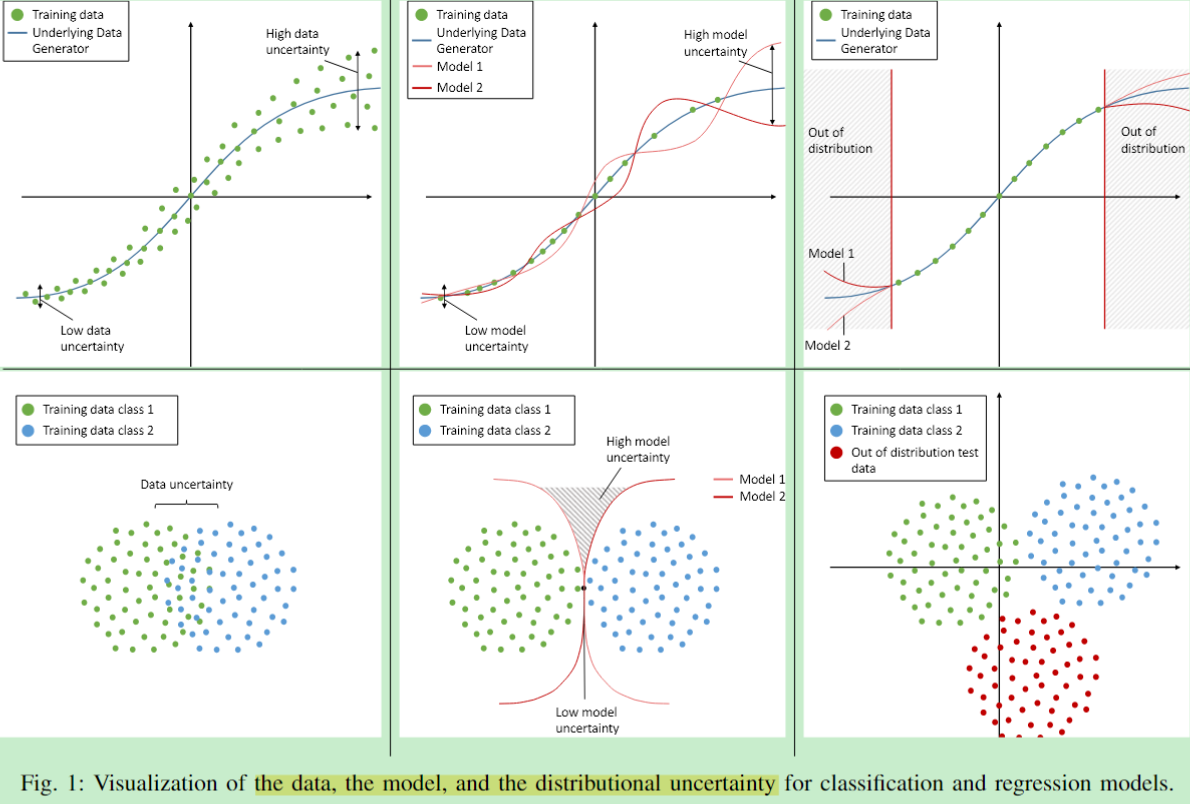
On the basis of the input data domain,(predictive) Uncertainty Classification:
- In-domain uncertainty,由于模型设计误差或者问题处理的复杂—> 通过增加训练集/训练过程质量解决
- Domain-shift uncertainty,由于真实世界情况的固有变化,例如遮挡造成的不确定性可以通过网络学习遮挡样本来解决(认知),但是部分如固有的运动无法解决(随机)
- Out-of-domain uncertainty,测试集完全与训练集数据不是一个分布,例如在猫狗数据上训练的分类网络让他去分类故障类型
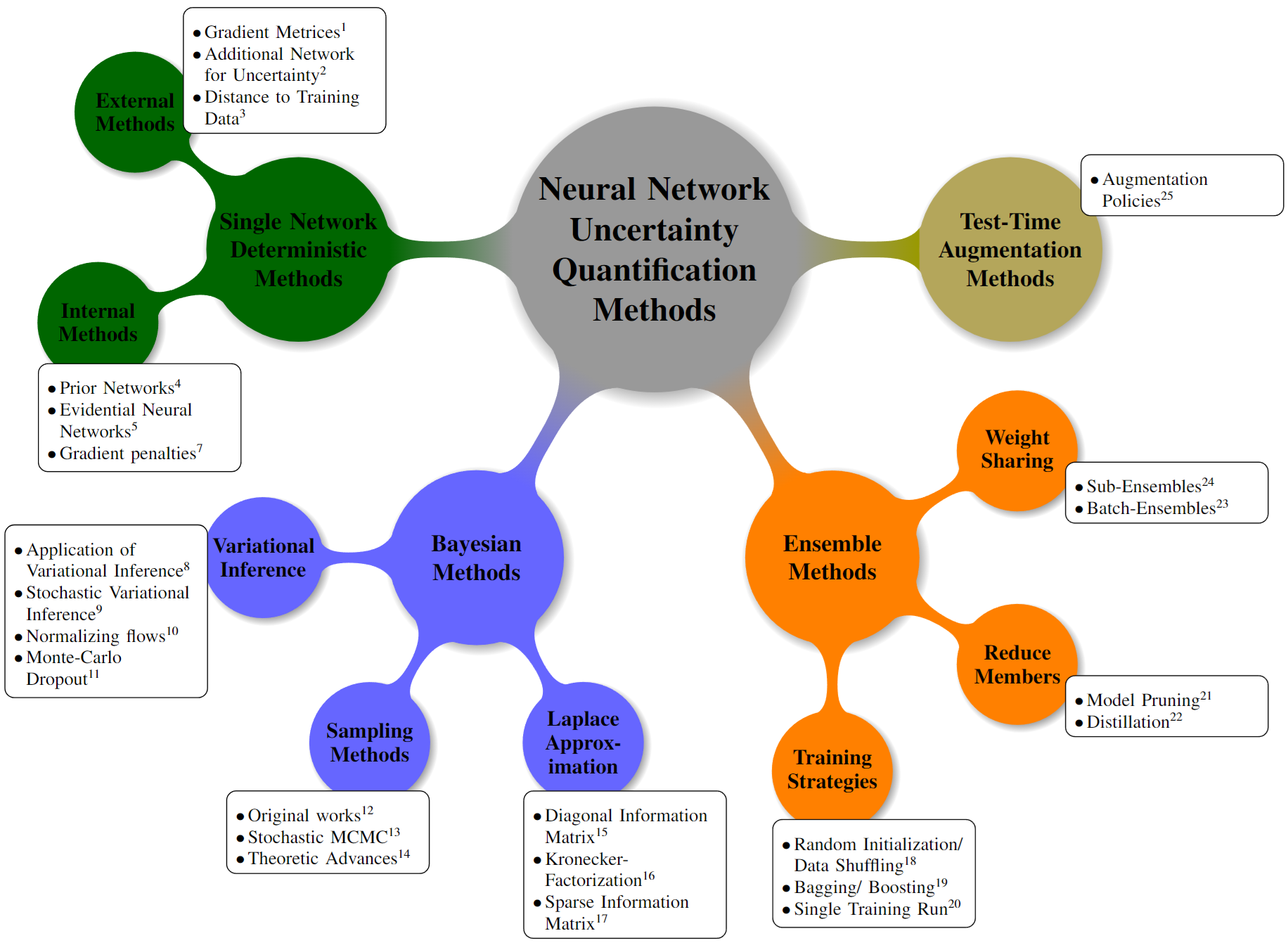
Uncertainty estimation: 与正常在预测中的数据不确定性部分(如分类网络预测的softmax output位每类概率,回归网络的显式标准差$\sigma$预测)不同,这些方法对模型不确定性进行建模,试图将其与数据不确定性分开,以获取数据不确定性的准确表示
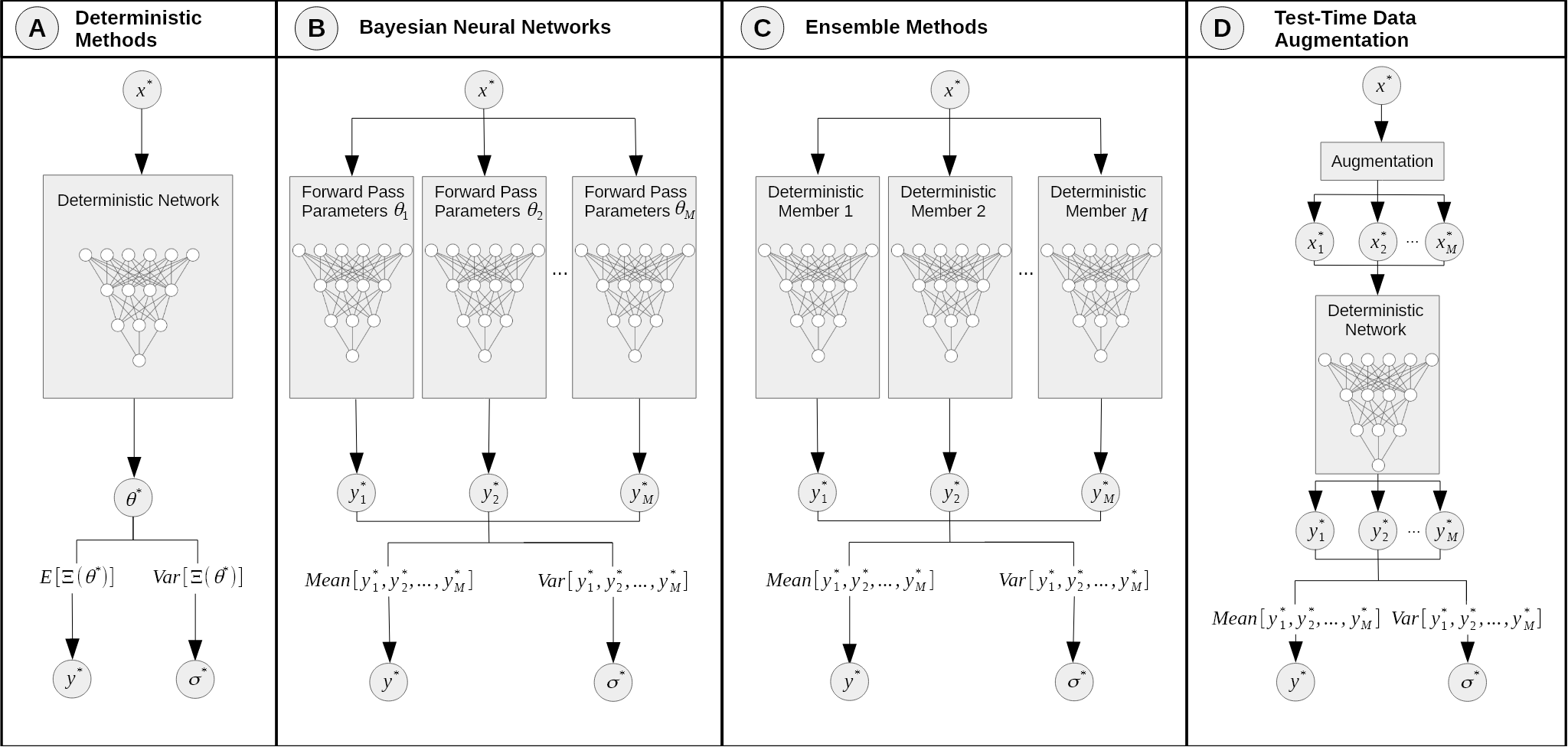
- Single Deterministic Methods
- Bayesian Neural Networks
- Ensemble Methods
- Test Time Augmentation
- Neural Network Uncertainty Quantification Approaches for Real Life Applications
Calibration Methods:
- Regularization methods applied during the training phase
- Post-processing methods applied after the training process of the DNN
- Neural network uncertainty estimation methods
quoFEM
Quantified Uncertainty with Optimization for the Finite Element Method (quoFEM) — Quantified Uncertainty with Optimization for the FEM documentation
When learning Bayesian Model Updating & TMCMC, find from mukeshramancha/transitional-mcmc: This repo contains the code of Transitional Markov chain Monte Carlo algorithm
Seminar
现代机器学习视角下的不确定性度量
[FAI] 清华 滕佳烨 | 现代机器学习视角下的不确定性度量 | ICLR 23_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
FAI-Seminar
之前的不确定性:Parameter Inference
神经网络的:Predictive Inference
Parameter Inference:(线性回归任务)
- $y=x^{\top}\beta^{*}+\epsilon,\epsilon{\sim}\mathcal{N}\left(0,\sigma^{2}I\right).$
- $\hat{\beta}=\left(X^{\top}X\right)^{-1}X^{\top}Y\sim\mathcal{N}\left(\beta^{*},\sigma^{2}\left(X^{\top}X\right)^{-1}\right).$
- Confidence Band $\mathcal{C}_{1-\alpha}(X)=\hat{\beta}\pm c_{\alpha}\sigma\left(X^{\top}X\right)^{-1/2},$
- 置信度$\alpha$,对应常数$c_{\alpha}$,则$\mathbb{P}\left(\beta^{*}\in\mathcal{C}_{1-\alpha}(X)\right)\geq1-\alpha.$
Predictive Inference:
由于神经网络的参数都是很难解释的,无法Parameter Inference,或者说无法通过简单的Parameter Inference得到:
$y=x^{\top}\beta^{}+\epsilon,\epsilon{\sim}\mathcal{N}\left(0,\sigma^{2}I\right).$能构造Parameter cb:$\mathcal{C}_{1-\alpha}(X)=\hat{\beta}\pm c_{\alpha}\sigma\left(X^{\top}X\right)^{-1/2},\beta^{}\in\mathcal{C}_{1-\alpha}(X)\mathrm{~whp}.$,然后根据$\beta^{*}$的band构造$y$的band
- 需要构造两次band
- parameter通常是是无意义的,其band也没意义
Predictive Inference定义:
给定一个在training set $\mathcal{D}=\{(X_{i},Y_{i})\}$上训练好的model $\mu$,以及一个置信度$\alpha$,构建一个置信band $\mathcal{C}_{1-\alpha}(\cdot;\mathcal{D},\mu)$,对任意测试point $(X^\prime,Y^\prime)$有:
$\mathbb{P}\left(Y^{\prime}\in\mathcal{C}_{1-\alpha}(X^{\prime};\mathcal{D},\mu)\right)\geq1-\alpha.$
Generalization(Validation Trick: 将验证集的loss当作测试集的loss)
$\mathbb{E}|\widehat{Y}-Y|\leq\epsilon$ 越小越好
Predictive Inference
$\mathbb{P}\left(Y^{\prime}\in\mathcal{C}_{1-\alpha}(X^{\prime};\mathcal{D},\mu)\right)\geq1-\alpha.$ 满足大于$1-\alpha$的band越小越好
Generalization(Validation Trick) —> Predictive Inference(Conformal Prediction):
- Training set上训练model
- Calibration set上测试model